Published On Aug 12, 2020
Today, we are going to talk about Kepler’s Laws of Planetary Motion.
Kepler’s laws of planetary motion are laws describing the motions of the planets in the solar system. They were derived by the German astronomer Johannes Kepler.
There are three laws of planetary motion. Let us talk about them one by one.
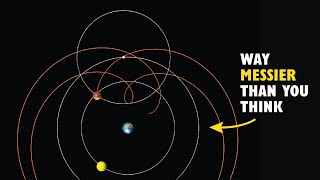
Kepler’s first law of planetary motion sometimes referred to as the law of ellipses, can be stated as “All planets move about the Sun in elliptical orbits, having the Sun as one of the foci.” This means that planets are orbiting the sun in a path described as an ellipse.
(Show picture of an ellipse with foci)
This is a picture of an ellipse. Suppose this ellipse is where the planet Earth moves. The Earth moves along the ellipse around the Sun. The Sun is located at either one of the foci of the ellipse.
Now, let us move on to the second law.
Kepler’s second law of planetary motion sometimes referred to as the law of equal areas, can be stated as “A radius vector joining any planet to the Sun sweeps out equal areas in equal lengths of time.”
The second law describes the speed at which any given planet will move while orbiting the sun. Know that when a planet is close to the sun, it moves fast but when a planet is far from the sun, it moves slowly. So if we draw an imaginary line of the movement of the planet and the sun for every month of the year, we can see that when the planet is close to the sun, it will form a wide but short triangle. And when the planet is far from the sun, it will form a thin but long triangle. The earth would have to adjust its movements in order to match the imaginary area.
Find out more by watching the video.
*Enjoy this fun and educational video from EarthPen
#KeplersLaws #Physics #EducationalVideo
CONTACT US
Email: [email protected]
Facebook Page: / earthpen
Youtube Channel: / @earthpen